However, before you could welcome abode most of these tweaks onto your device, you will first have to gain administrative access, in other words, root your Xiaomi/Redmi/Poco device via Magisk Patched boot.img file. And in this guide, we will show you how to do just that. So without further ado, let’s get started.
Benefits and Risks of Rooting Xiaomi/Poco/Redmi
Once you root your device by flashing the Magisk patched boot.img via Fastboot Commands, you will be in a position to try out a plethora of customizations on your device. These include the likes of flashing custom ROMs, installing a custom recovery like TWRP, or flashing a custom kernel. Along the same lines, you could also flash Magisk Modules, Xposed Framework, Substratum Themes, Viper4Android, and the likes. However, this is just one side of the story.
Carrying out this process also has its downsides. First off, the process requires an unlocked bootloader. Doing so will wipe off all the data and could nullify the device’s warranty as well. Likewise, WideVine L1 will be degraded to L3, resulting in the inability to stream Netflix in HD [FIXED]. Then the SafetyNet will be triggered [FIXED], which might cause issues with banking apps [FIXED]. If that’s well and good, then let’s get started with the steps to root your device.
IMPORTANT: Rooting Android 13 is different from previous OS!
Till Android 12, you just need to extract the boot.img from the sock firmware, patch it via Magisk, boot your device using the patched file via the fastboot boot command, and then use Magisk’s Direct Install feature to complete the process. However, beginning with Android 13, this process is slightly different now. For the devices that ship with Android 13 out of the box, such as Xiaomi 13, you don’t have to use the boot.img file.
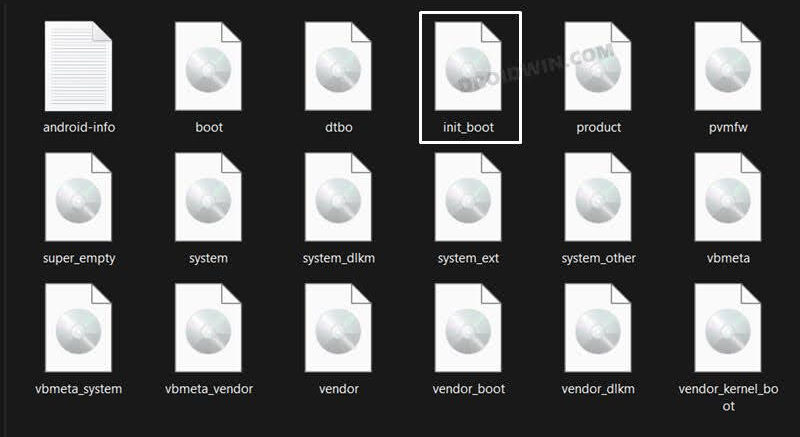
Instead, you have to use init_boot.img file which could be extracted from the stock firmware itself. After this, you could patch the init_boot via Magisk and flash it via Fastboot [as of now, you cannot temporarily boot patched init_boot via Fastboot, so you cannot use Magisk’s Direct Install either. Rather, you will have to directly flash the patched init_boot via the fastboot flash command.
However, do keep in mind that this rule only applies to the devices that come with Android 13 out of the box, if your device came with an older version of OS and has subsequently received the Android 13 update, such as Poco F4, then you don’t have to use the init_boot file, rather you should still use the older method of rooting via patched boot.img.
How to Root any Xiaomi/Redmi/Poco via Magisk
The below instructions are listed under separate sections for ease of understanding. Make sure to follow the same sequence as mentioned. Droidwin and its members wouldn’t be held responsible in case of a thermonuclear war, your alarm doesn’t wake you up, or if anything happens to your device and data by performing the below steps.
STEP 1: Install Android SDK
First and foremost, you will have to install the Android SDK Platform Tools on your PC. This is the official ADB and Fastboot binary provided by Google and is the only recommended one. So download it and then extract it to any convenient location on your PC. Doing so will give you the platform tools folder, which will be used throughout this guide to root your Xiaomi/Redmi/Poco.
STEP 2: Enable USB Debugging and OEM Unlocking
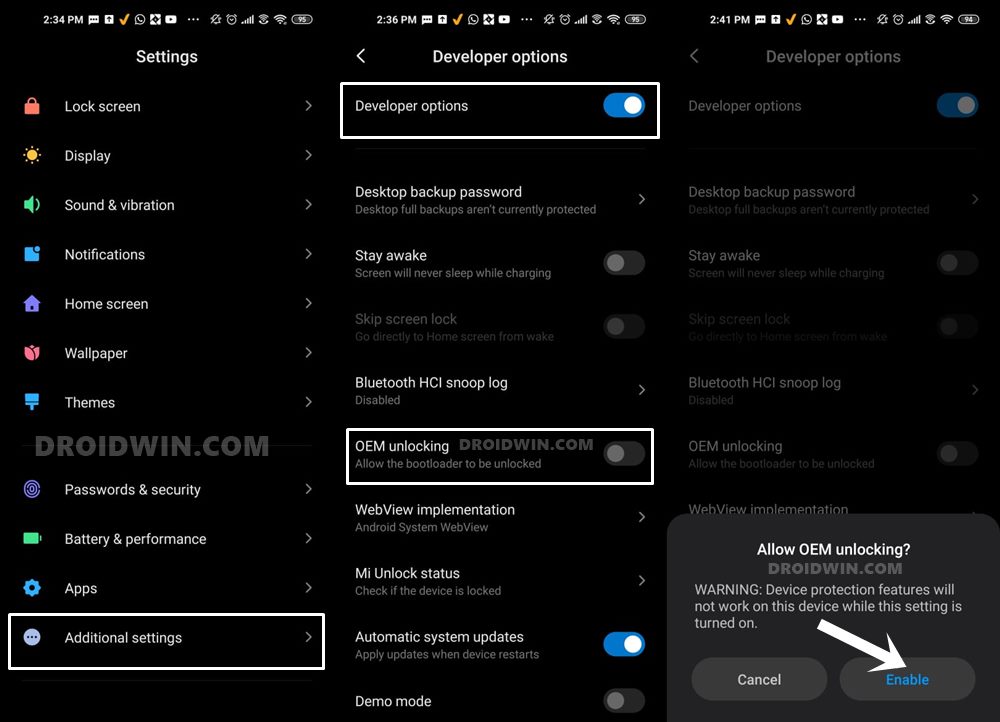
Next up, you will also have to enable USB Debugging and OEM Unlocking on your device. The former will make your device recognizable by the PC in ADB mode. This will then allow you to boot your device to Fastboot Mode. On the other hand, OEM Unlocking is required to carry out the bootloader unlocking process.
So head over to Settings > About Phone > Tap on MIUI Number 7 times > Go back to Settings > System > Advanced > Developer Options > Enable USB Debugging and OEM Unlocking.
STEP 3: Unlock Xiaomi/Redmi/Poco Bootloader
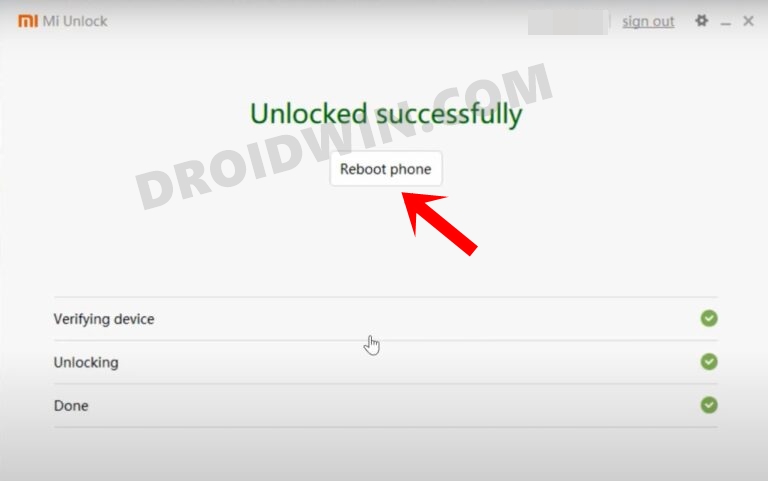
Next up, you will need to unlock the device’s bootloader. However, doing so will wipe off all the data and could nullify the device’s warranty as well. So if that’s all well and good, then please refer to our guide on How to Unlock the Bootloader on any Xiaomi Device. Once that is done, you may move over to the next step to root your Xiaomi/Poco/Redmi via Magisk.
STEP 4: Download Xiaomi Fastboot ROM
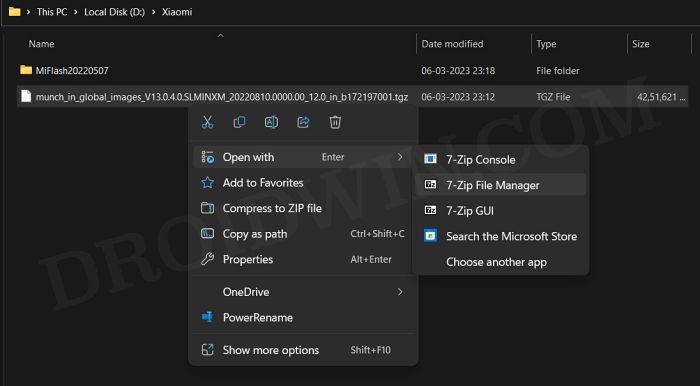
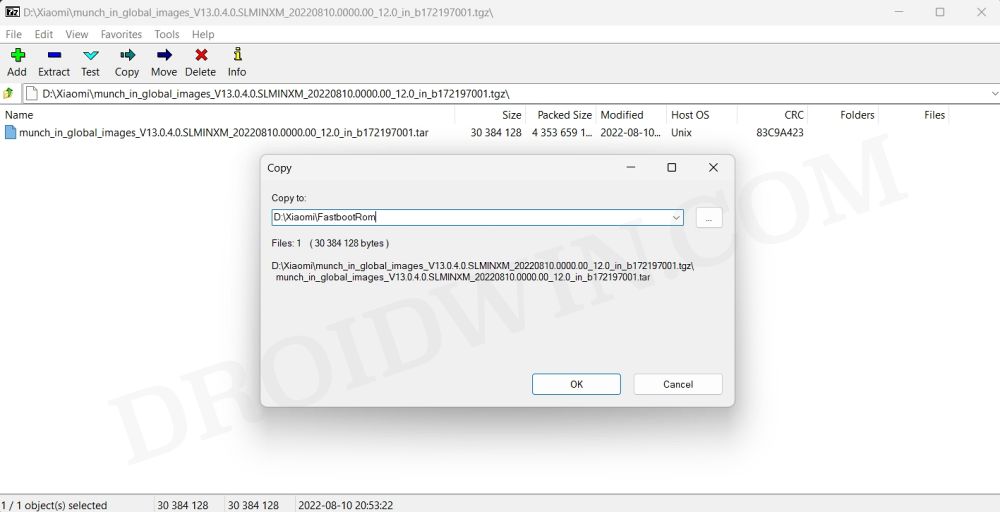
Next up, you will have to download the Fastboot ROM for your device. Make sure to download the same version that is currently installed on your device (you could verify the same from your device’s Build Number). As far as the downloading source is concerned, you could get it from the official MIUI site or a third-party site like Xiaomi Firmware Updater (if the official website is blocked in your region).
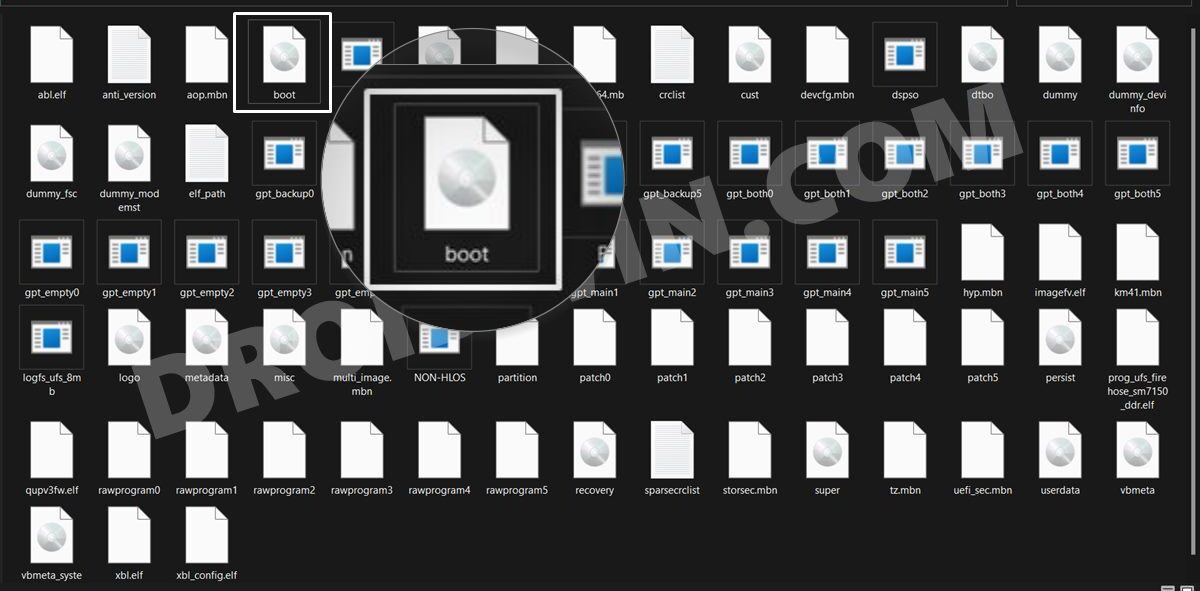
STEP 5: Get Xiaomi/Poco/Redmi Stock Boot.img
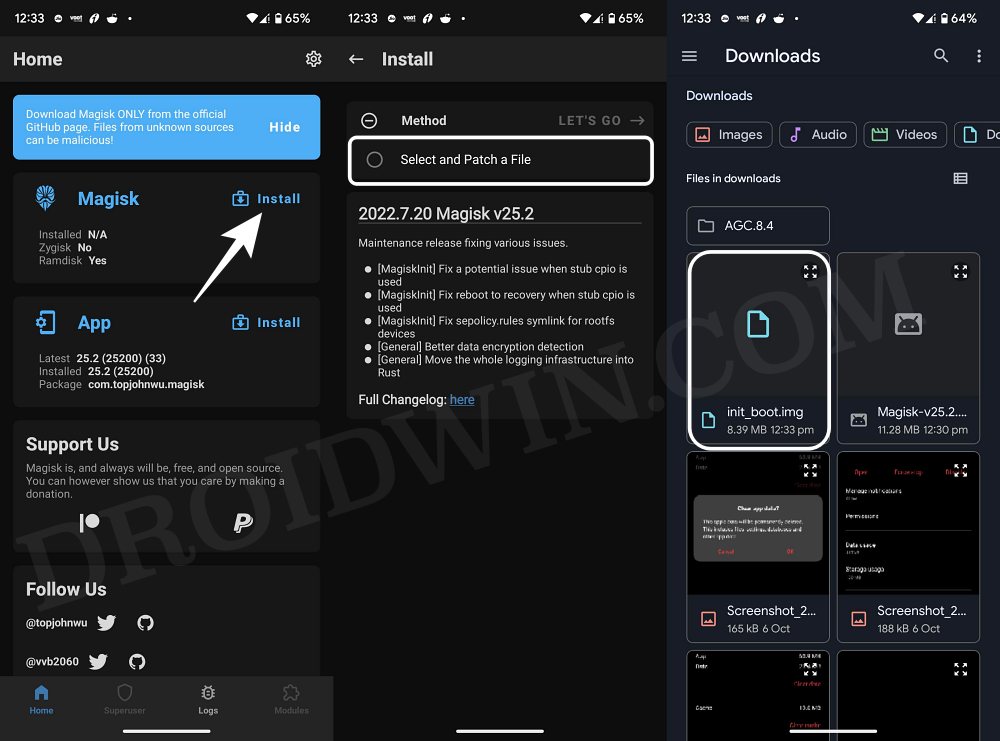
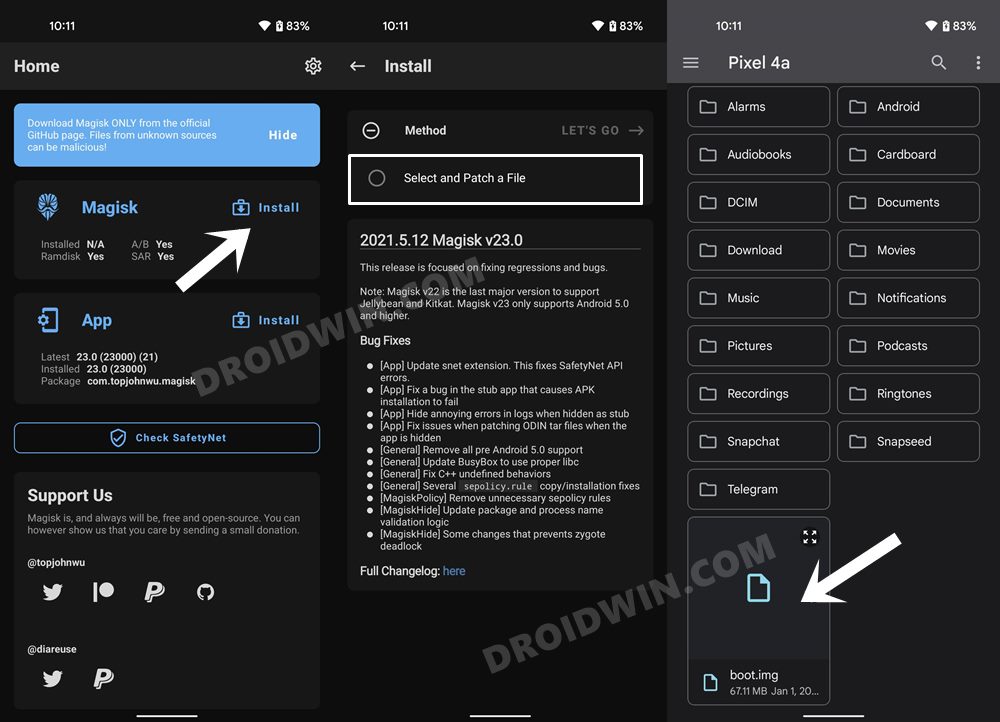
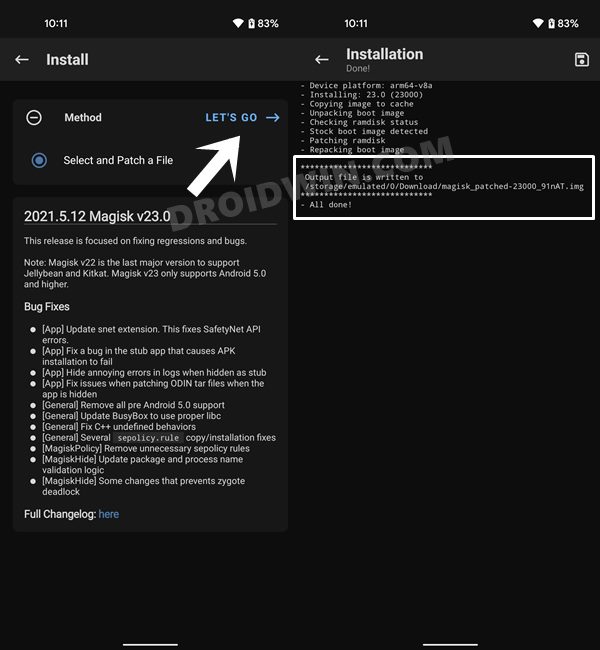
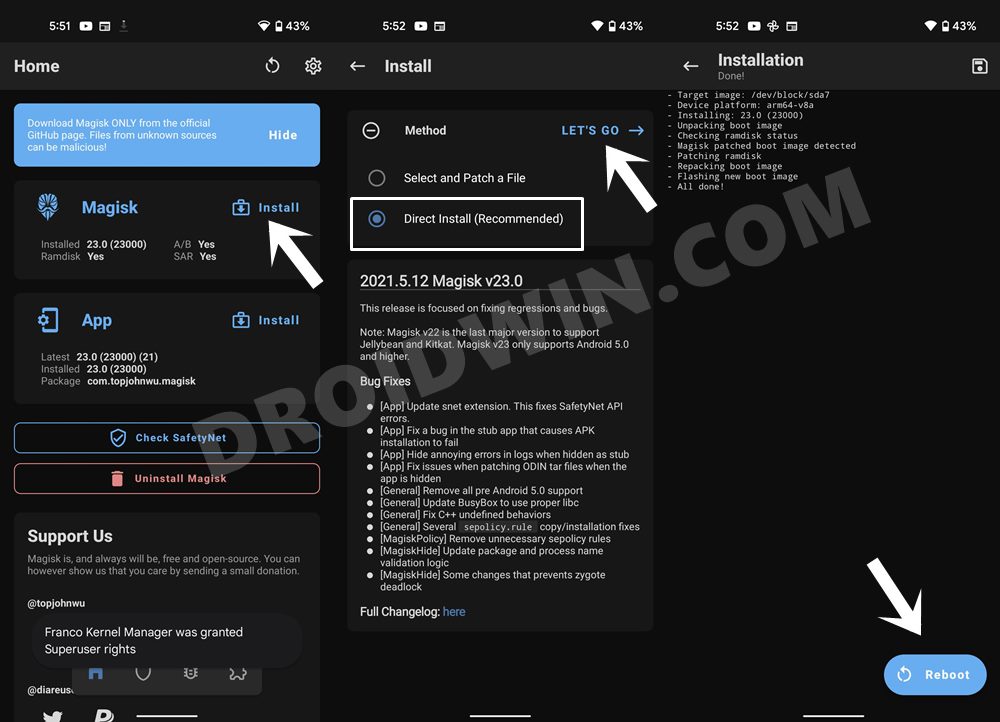
STEP 6: Patch Boot/Init_boot via Magisk
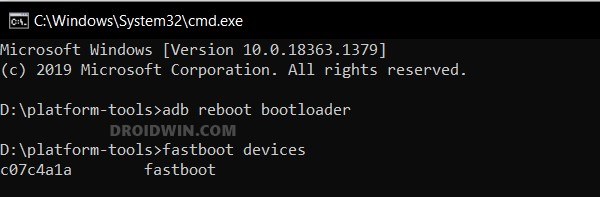
STEP 7: Boot Xiaomi/Poco/Redmi to Fastboot Mode
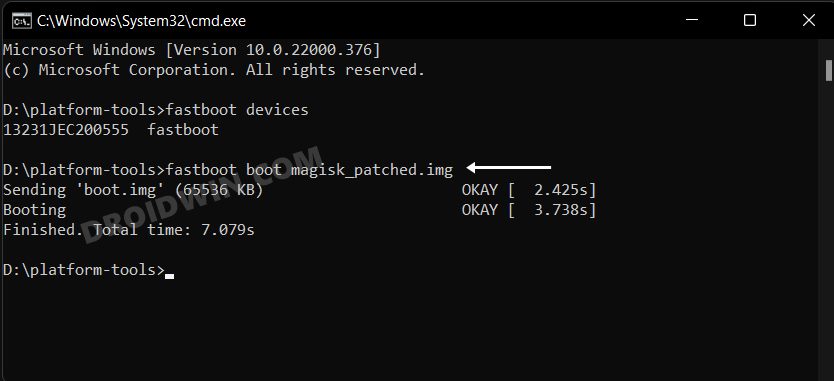
STEP 8A: Root Xiaomi via Magisk Patched Boot
This step is applicable for those devices that came with an OS version older than Android 13 and have since received an Android 13 update.
STEP 8B: Root Xiaomi via Magisk Patched Init_Boot
This step is applicable for those devices that came with Android 13 out of the box. That’s it. These were the steps to root your Xiaomi/Poco/Redmi via Magisk. If you have any queries concerning the aforementioned steps, do let us know in the comments section. We will get back to you with a solution at the earliest. There also exists a method to root your Xiaomi device by directly flashing the Magisk patched boot file. However, that is usually a risky approach and should be avoided. The above approach of first booting the patched file and then permanently flashing it via Direct Install of Magisk is the fail-safe method that you should opt for. This is because by first temporarily booting via the patched file, we could check if everything is working well and good. If it doesn’t, then you just need to do a simple reboot and the patched boot will be replaced by stock and your device will be booted to the OS. On the other hand, if everything works well and good, then you could permanently flash the patched boot via the Direct Install method.
Case 1: While using Fastboot Boot Magisk Patched
If your device is stuck in bootloop while temporarily booting the magisk patched boot.img, then just perform a restart and it will replace the patched boot.img with the stock boot. And once you are in the OS, reverify the boot.img file that you had used and then retry the flashing process.
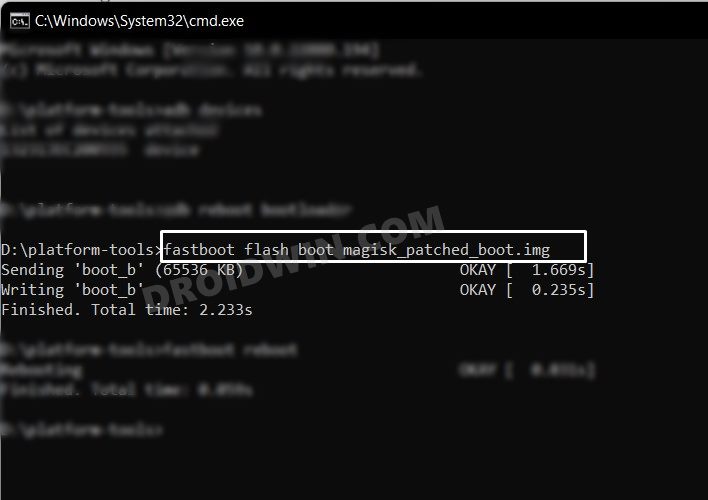
Case 2: While using Fastboot Flash Patched Boot/Init_boot
On the other hand, if you had permanently flashed it, then you will have to flash the stock boot.img file as instructed below:
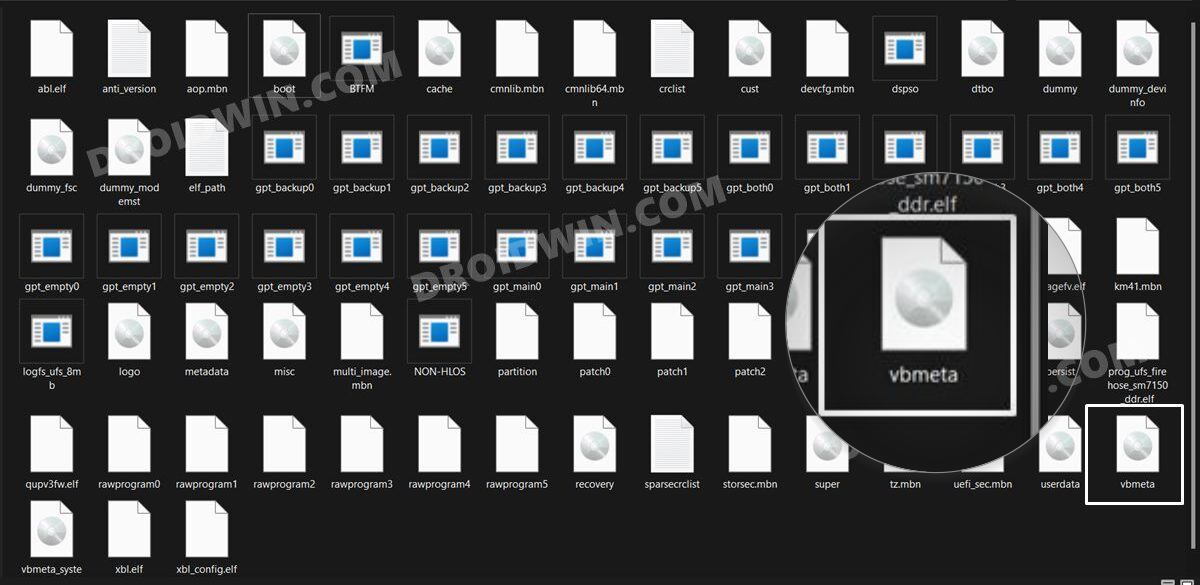
Case 3: Disable DM Verity
If none of the aforementioned methods spelled out success, then you’ll have to disable the verity checks by flashing the vbmeta file. Here’s how it could be done:
How to Pass SafetyNet on Rooted Android 12/Android 13How to Hide Root from Apps via Magisk DenyList [Android 12]Enable Choose Update Package | Reboot to Recovery Mode: MIUI XiaomiHow to Enable VoLTE and VoWiFi on Xiaomi (Root/Non-Root)
About Chief Editor